模拟退火
最近在看数学建模= =
先学学智能算法.
模拟退火算法可以用来求解最优化问题.
模拟退火算法认识
爬山算法也是一个用来求解最优化问题的算法,每次都向着当前上升最快的方向往上爬,但是初始化不同可能
会得到不同的局部最优值,模拟退火算法就可能跳出这种局部最优解的限制。模拟退火算法是模拟热力学系统
中的退火过程。在退火过程中是将目标函数作为能量函数。大致过程如下初始高温 => 温度缓慢下降=> 终止在低温 (这时能量函数达到最小,目标函数最小)
在热力学中的退火过程大致是变温物体缓慢降温而达到分子之间能量最低的状态。设热力学系统S中有有限个且离散的n个状态,状态i的能量为Ei,在温度Tk下,经过一段时间达到热平衡,这时处于i状态的概率为
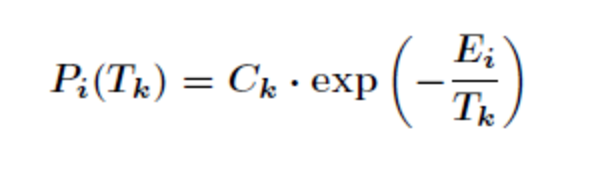
模拟退火算法也是贪心算法,但是在其过程中引入了随机因素,以一定的概率接受一个比当前解要差的解,并且
这个概率随着时间的推移而逐渐降低。模拟退火算法描述
若
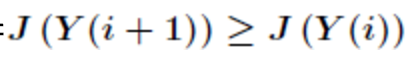 ,即移动后得到更优的解,那么总是接受改移动。
,即移动后得到更优的解,那么总是接受改移动。
若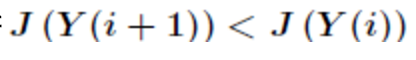 ,即移动后得到更差的解,则以一定的概率接受该移动,并且这个概率随时间推移
,即移动后得到更差的解,则以一定的概率接受该移动,并且这个概率随时间推移
逐渐降低。这个概率表示为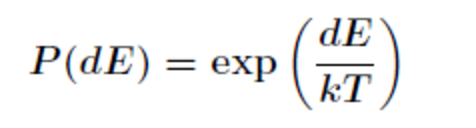
由于是退火过程,所以dE < 0,这个公式说明了温度越高出现一次能量差为dE的降温概率就越大,温度越低,
出现降温的概率就越小,由于dE总是小于0,所以P(dE)取值在0到1之间。伪码如下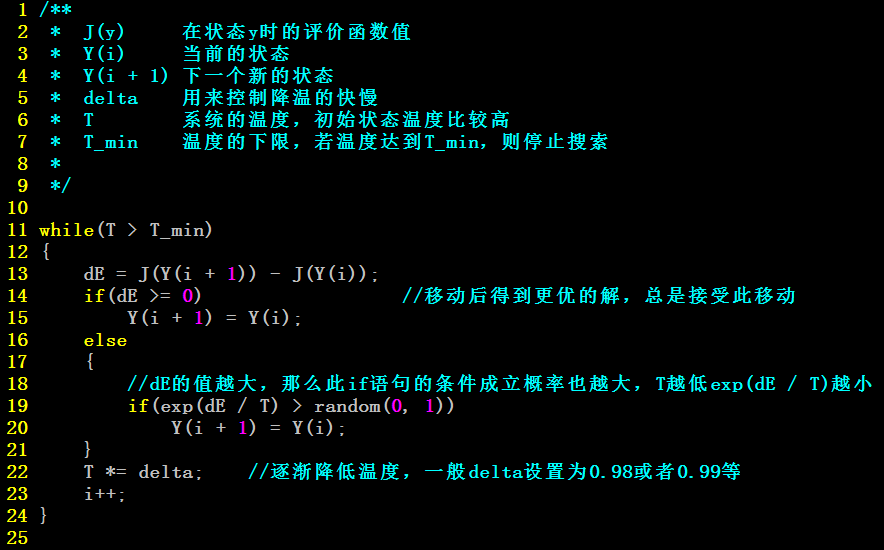
poj2420
A Star not a Tree?
Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K
Total Submissions: 5215 Accepted: 2488
Description
Luke wants to upgrade his home computer network from 10mbs to 100mbs. His existing network uses 10base2 (coaxial) cables that allow you to connect any number of computers together in a linear arrangement. Luke is particulary proud that he solved a nasty NP-complete problem in order to minimize the total cable length.
Unfortunately, Luke cannot use his existing cabling. The 100mbs system uses 100baseT (twisted pair) cables. Each 100baseT cable connects only two devices: either two network cards or a network card and a hub. (A hub is an electronic device that interconnects several cables.) Luke has a choice: He can buy 2N-2 network cards and connect his N computers together by inserting one or more cards into each computer and connecting them all together. Or he can buy N network cards and a hub and connect each of his N computers to the hub. The first approach would require that Luke configure his operating system to forward network traffic. However, with the installation of Winux 2007.2, Luke discovered that network forwarding no longer worked. He couldn’t figure out how to re-enable forwarding, and he had never heard of Prim or Kruskal, so he settled on the second approach: N network cards and a hub.
Luke lives in a loft and so is prepared to run the cables and place the hub anywhere. But he won’t move his computers. He wants to minimize the total length of cable he must buy.
Input
The first line of input contains a positive integer N <= 100, the number of computers. N lines follow; each gives the (x,y) coordinates (in mm.) of a computer within the room. All coordinates are integers between 0 and 10,000.
Output
Output consists of one number, the total length of the cable segments, rounded to the nearest mm.
Sample Input
4
0 0
0 10000
10000 10000
10000 0
Sample Output
28284
c++代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#define N 1005
#define eps 1e-8 //搜索停止条件阀值
#define INF 1e99
#define delta 0.98 //温度下降速度
#define T 100 //初始温度
using namespace std;
int dx[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int dy[4] = {-1, 1, 0, 0}; //上下左右四个方向
struct Point
{
double x, y;
};
Point p[N];
double dist(Point A, Point B)
{
return sqrt((A.x - B.x) * (A.x - B.x) + (A.y - B.y) * (A.y - B.y));
}
double GetSum(Point p[], int n, Point t)
{
double ans = 0;
while(n--)
ans += dist(p[n], t);
return ans;
}
double Search(Point p[], int n)
{
Point s = p[0]; //随机初始化一个点开始搜索
double t = T; //初始化温度
double ans = INF; //初始答案值
while(t > eps)
{
bool flag = 1;
while(flag)
{
flag = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) //上下左右四个方向
{
Point z;
z.x = s.x + dx[i] * t;
z.y = s.y + dy[i] * t;
double tp = GetSum(p, n, z);
if(ans > tp)
{
ans = tp;
s = z;
flag = 1;
}
}
}
t *= delta;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%lf %lf", &p[i].x, &p[i].y);
printf("%.0lf\n", Search(p, n));
}
return 0;
}
题目:平面上给定n条线段,找出一个点,使这个点到这n条线段的距离和最小。
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#define N 1005
#define eps 1e-8 //搜索停止条件阀值
#define INF 1e99
#define delta 0.98 //温度下降速度
#define T 100 //初始温度
using namespace std;
int dx[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int dy[4] = {-1, 1, 0, 0}; //上下左右四个方向
struct Point
{
double x, y;
};
Point s[N], t[N];
double cross(Point A, Point B, Point C)
{
return (B.x - A.x) * (C.y - A.y) - (B.y - A.y) * (C.x - A.x);
}
double multi(Point A, Point B, Point C)
{
return (B.x - A.x) * (C.x - A.x) + (B.y - A.y) * (C.y - A.y);
}
double dist(Point A, Point B)
{
return sqrt((A.x - B.x) * (A.x - B.x) + (A.y - B.y) * (A.y - B.y));
}
double GetDist(Point A, Point B, Point C)
{
if(dist(A, B) < eps) return dist(B, C);
if(multi(A, B, C) < -eps) return dist(A, C);
if(multi(B, A, C) < -eps) return dist(B, C);
return fabs(cross(A, B, C) / dist(A, B));
}
double GetSum(Point s[], Point t[], int n, Point o)
{
double ans = 0;
while(n--)
ans += GetDist(s[n], t[n], o);
return ans;
}
double Search(Point s[], Point t[], int n, Point &o)
{
o = s[0];
double tem = T;
double ans = INF;
while(tem > eps)
{
bool flag = 1;
while(flag)
{
flag = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) //上下左右四个方向
{
Point z;
z.x = o.x + dx[i] * tem;
z.y = o.y + dy[i] * tem;
double tp = GetSum(s, t, n, z);
if(ans > tp)
{
ans = tp;
o = z;
flag = 1;
}
}
}
tem *= delta;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%lf %lf %lf %lf", &s[i].x, &s[i].y, &t[i].x, &t[i].y);
Point o;
double ans = Search(s, t, n, o);
printf("%.1lf %.1lf %.1lf\n", o.x, o.y, ans);
}
return 0;
}
最小包含球问题求解
题目:http://poj.org/problem?id=2069
题意:给定三维空间的n点,找出一个半径最小的球把这些点全部包围住。
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define N 55
#define eps 1e-7
#define T 100
#define delta 0.98
#define INF 1e99
using namespace std;
struct Point
{
double x, y, z;
};
Point p[N];
double dist(Point A, Point B)
{
return sqrt((A.x - B.x) * (A.x - B.x) + (A.y - B.y) * (A.y - B.y) + (A.z - B.z) * (A.z - B.z));
}
double Search(Point p[], int n)
{
Point s = p[0];
double t = T;
double ans = INF;
while(t > eps)
{
int k = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if(dist(s, p[i]) > dist(s, p[k]))
k = i;
double d = dist(s, p[k]);
ans = min(ans, d);
s.x += (p[k].x - s.x) / d * t;
s.y += (p[k].y - s.y) / d * t;
s.z += (p[k].z - s.z) / d * t;
t *= delta;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(cin >> n && n)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> p[i].x >> p[i].y >> p[i].z;
double ans = Search(p, n);
printf("%.5lf\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
函数最值问题求解
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2899
题意:给出方程,其中,输入,求的最小值。
分析:本题可以用经典的二分法求解,这种方法比较简单,就不说了。主要来说模拟退火做法。
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#define ITERS 10
#define T 100
#define eps 1e-8
#define delta 0.98
#define INF 1e99
using namespace std;
double x[ITERS];
int Judge(double x, double y)
{
if(fabs(x - y) < eps) return 0;
return x < y ? -1 : 1;
}
double Random()
{
double x = rand() * 1.0 / RAND_MAX;
if(rand() & 1) x *= -1;
return x;
}
double F(double x, double y)
{
return 6 * x * x * x * x * x * x * x + 8 * x * x * x * x * x * x + 7 * x * x * x + 5 * x * x - y * x;
}
void Init()
{
for(int i = 0; i < ITERS; i++)
x[i] = fabs(Random()) * 100;
}
double SA(double y)
{
double ans = INF;
double t = T;
while(t > eps)
{
for(int i = 0; i < ITERS; i++)
{
double tmp = F(x[i], y);
for(int j = 0; j < ITERS; j++)
{
double _x = x[i] + Random() * t;
if(Judge(_x, 0) >= 0 && Judge(_x, 100) <= 0)
{
double f = F(_x, y);
if(tmp > f)
x[i] = _x;
}
}
}
t *= delta;
}
for(int i = 0; i < ITERS; i++)
ans = min(ans, F(x[i], y));
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--)
{
double y;
scanf("%lf", &y);
srand(time(NULL));
Init();
printf("%.4lf\n", SA(y));
}
return 0;
}
TSP问题求解
TSP问题是一个NP问题,但是可以求近似解,通过模拟退火算法实现,代码如下
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#define N 30 //城市数量
#define T 3000 //初始温度
#define EPS 1e-8 //终止温度
#define DELTA 0.98 //温度衰减率
#define LIMIT 10000 //概率选择上限
#define OLOOP 1000 //外循环次数
#define ILOOP 15000 //内循环次数
using namespace std;
//定义路线结构体
struct Path
{
int citys[N];
double len;
};
//定义城市点坐标
struct Point
{
double x, y;
};
Path path; //记录最优路径
Point p[N]; //每个城市的坐标
double w[N][N]; //两两城市之间路径长度
int nCase; //测试次数
double dist(Point A, Point B)
{
return sqrt((A.x - B.x) * (A.x - B.x) + (A.y - B.y) * (A.y - B.y));
}
void GetDist(Point p[], int n)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
w[i][j] = w[j][i] = dist(p[i], p[j]);
}
void Input(Point p[], int &n)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%lf %lf", &p[i].x, &p[i].y);
}
void Init(int n)
{
nCase = 0;
path.len = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
path.citys[i] = i;
if(i != n - 1)
{
printf("%d--->", i);
path.len += w[i][i + 1];
}
else
printf("%d\n", i);
}
printf("\nInit path length is : %.3lf\n", path.len);
}
void Print(Path t, int n)
{
printf("Path is : ");
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if(i != n - 1)
printf("%d-->", t.citys[i]);
else
printf("%d\n", t.citys[i]);
}
printf("\nThe path length is : %.3lf\n", t.len);
}
Path GetNext(Path p, int n)
{
Path ans = p;
int x = (int)(n * (rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0)));
int y = (int)(n * (rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0)));
while(x == y)
{
x = (int)(n * (rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0)));
y = (int)(n * (rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0)));
}
swap(ans.citys[x], ans.citys[y]);
ans.len = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
ans.len += w[ans.citys[i]][ans.citys[i + 1]];
cout << "nCase = " << nCase << endl;
Print(ans, n);
nCase++;
return ans;
}
void SA(int n)
{
double t = T;
srand(time(NULL));
Path curPath = path;
Path newPath = path;
int P_L = 0;
int P_F = 0;
while(1) //外循环,主要更新参数t,模拟退火过程
{
for(int i = 0; i < ILOOP; i++) //内循环,寻找在一定温度下的最优值
{
newPath = GetNext(curPath, n);
double dE = newPath.len - curPath.len;
if(dE < 0) //如果找到更优值,直接更新
{
curPath = newPath;
P_L = 0;
P_F = 0;
}
else
{
double rd = rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0);
if(exp(dE / t) > rd && exp(dE / t) < 1) //如果找到比当前更差的解,以一定概率接受该解,并且这个概率会越来越小
curPath = newPath;
P_L++;
}
if(P_L > LIMIT)
{
P_F++;
break;
}
}
if(curPath.len < newPath.len)
path = curPath;
if(P_F > OLOOP || t < EPS)
break;
t *= DELTA;
}
}
int main()
{
freopen("TSP.data", "r", stdin);
int n;
Input(p, n);
GetDist(p, n);
Init(n);
SA(n);
Print(path, n);
printf("Total test times is : %d\n", nCase);
return 0;
}